What is Multicloud?
Table of Contents

Multicloud refers to using multiple cloud computing services from different providers within a single network architecture to fulfill an organization’s IT needs.
A multicloud environment typically comprises two or more public clouds, two or more private clouds, or a combination of both. However, the common practice is to leverage services from more than one public cloud provider simultaneously.
This strategy differs from a hybrid cloud, which integrates private and public clouds to function as a cohesive system. In contrast, multicloud emphasizes the use of multiple cloud services from different vendors without necessarily integrating them into a unified infrastructure.
The core objective of a multicloud strategy is to provide flexibility, allowing organizations to select best-in-class services from different vendors based on specific needs. This approach enables enterprises to optimize performance, cost, and compliance by matching workloads to the most suitable cloud services.
One significant advantage of adopting a multicloud approach is the avoidance of vendor lock-in. By not relying on a single cloud provider, organizations can mitigate risks associated with service outages, pricing changes, or technological limitations inherent to a specific vendor. This flexibility ensures greater control over the IT ecosystem and the ability to adapt to evolving business requirements.
The adoption of multicloud strategies is rapidly transforming how companies manage their IT infrastructure. According to Gartner, by 2025, over 85% of organizations will embrace a cloud-first principle, with more than 50% relying on multicloud strategies to drive business innovation and digital transformation.
What is the Difference Between Multicloud and Hybrid Cloud?
The main difference between multicloud and hybrid cloud lies in their architecture and scope.
- Hybrid cloud integrates different types of cloud infrastructures (private and public) into a unified architecture with shared control and workflows.
- Multicloud distributes workloads across multiple independent cloud services, typically from different vendors, without architectural integration.
Hybrid cloud is defined by its integrated architecture: it combines private infrastructure, such as on-premises data centers or private clouds, with public cloud platforms in a single, interconnected environment. These components are unified through orchestration and integration, enabling seamless data and workload mobility between private and public environments.
The scope of hybrid cloud is centered on creating a cohesive system that supports real-time interoperability, which is beneficial for scenarios that demand strict compliance, low latency, or hybrid data processing.
Multicloud, on the other hand, is architected around separation rather than integration. It refers to the use of services from multiple cloud providers — most commonly more than one public cloud vendor (e.g., AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) — without the requirement of interconnection. Each cloud environment in a multicloud setup typically functions independently, handling specific tasks or workloads according to business needs.
The scope of multicloud emphasizes flexibility and diversification, allowing organizations to leverage the strengths of various providers while avoiding dependence on a single vendor.
What are the Benefits of Multicloud?

Multicloud offers several benefits, including minimizing vendor dependency, strengthening system resilience, optimizing costs, improving performance, enabling service flexibility and access to best-in-class tools, supporting low-latency and regulatory-aligned deployments, enhancing data security and risk management, and reducing unauthorized IT usage.
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In
Avoiding vendor lock-in is a key benefit of multicloud because it gives enterprises greater control over their cloud infrastructure and service choices. By not relying on a single cloud provider, organizations can freely choose the best technologies available across different platforms, adapt more quickly to changing business needs, and avoid being constrained by a provider’s pricing, performance, or feature limitations.
Enhanced Resilience
Enhanced resilience reduces the risk of downtime by distributing workloads across multiple cloud environments. This approach ensures that if one provider experiences an outage, services can continue uninterrupted by shifting operations to other active platforms.
An enterprise load balancer can intelligently route traffic across different clouds, automatically shifting workloads away from degraded or failed instances to healthy ones.
For instance, a multicloud disaster recovery strategy allows workloads to be redirected to another cloud provider in the event of an outage, removing the risk of a single point of failure and inherently reducing the risk of data loss and downtime.
Organizations adopting multicloud approaches have reported significant improvements in resilience. According to a study by the International Data Corporation (IDC), organizations that adopt multicloud approaches can reduce downtime by up to 60%, highlighting the advantages of integrating diverse cloud services to secure critical information.
Companies like Netflix utilize multicloud environments to ensure high availability and fault tolerance, distributing processing and streaming workloads across different cloud service providers to maintain continuous service even during peak times or unforeseen outages.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency enables enterprises to select the most economically viable services for each specific workload. By comparing pricing models across multiple cloud providers and aligning each task with the most cost-effective option, organizations can better manage their budgets and avoid overspending.
Performance Optimization
Performance optimization in a multicloud environment allows enterprises to run each application in the most suitable cloud setting. Mission-critical workloads can be placed on high-performance platforms to ensure speed and reliability, while less demanding tasks can run on more economical services.
Flexibility and Best-of-Breed Services
A key benefit of a multicloud architecture is the flexibility it provides in selecting best-of-breed services from multiple cloud vendors. Enterprises are not limited to a one-size-fits-all solution and can tailor their cloud strategy to match specific business and technical requirements.
For example:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers powerful compute services (like EC2) and a wide range of data analytics tools, making it ideal for high-performance computing and data-driven applications.
- Microsoft Azure provides strong enterprise integration with Microsoft products and robust support for hybrid multicloud platforms, which is beneficial for companies already embedded in the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) stands out with its advanced AI/ML capabilities and efficient data processing tools like BigQuery, making it a preferred option for machine learning workloads and large-scale data analytics.
By combining the strengths of these different providers, enterprises can assign workloads based on what each vendor does best. For instance, they might run AI models on GCP, host enterprise software on Azure, and manage large-scale compute operations on AWS.
Proximity, Reduced Latency, and Compliance
A multicloud strategy allows enterprises to deploy applications and services in cloud regions that are geographically closest to their end users. By selecting local cloud providers or regional data centers, businesses can significantly reduce latency, resulting in faster response times and a smoother user experience, especially important for latency-sensitive applications like streaming, gaming, or real-time analytics.
Additionally, leveraging multiple cloud providers in specific regions helps organizations meet local regulatory requirements and data sovereignty laws. This is especially critical in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, where data must remain within certain jurisdictions to comply with legal frameworks and industry standards.
Data Protection and Risk Mitigation
Multicloud environments enhance data protection by distributing data and workloads across multiple independent cloud providers, reducing the risk of data loss or corruption from a single point of failure. This geographic and provider-level diversity ensures that if one cloud experiences an outage, breach, or disaster, critical data remains safe and accessible through other clouds.
Additionally, multicloud supports a robust data protection plan by enabling enterprises to implement tailored backup, disaster recovery, and encryption strategies across different platforms. Organizations can replicate data across clouds, use varied security features offered by each provider, and maintain multiple copies to ensure business continuity.
Combating Shadow IT
Shadow IT refers to the use of IT systems, software, or cloud services within an organization without the approval or knowledge of the IT department. It often arises when employees independently adopt tools they believe better meet their needs, which can lead to security risks, compliance issues, and unmanaged costs.
A multicloud strategy helps combat shadow IT by offering authorized, flexible options that satisfy diverse user requirements across the enterprise. By providing access to a variety of trusted cloud services through official channels, organizations can reduce the temptation for employees to seek unauthorized solutions.
How to Implement and Manage Multicloud Environments?
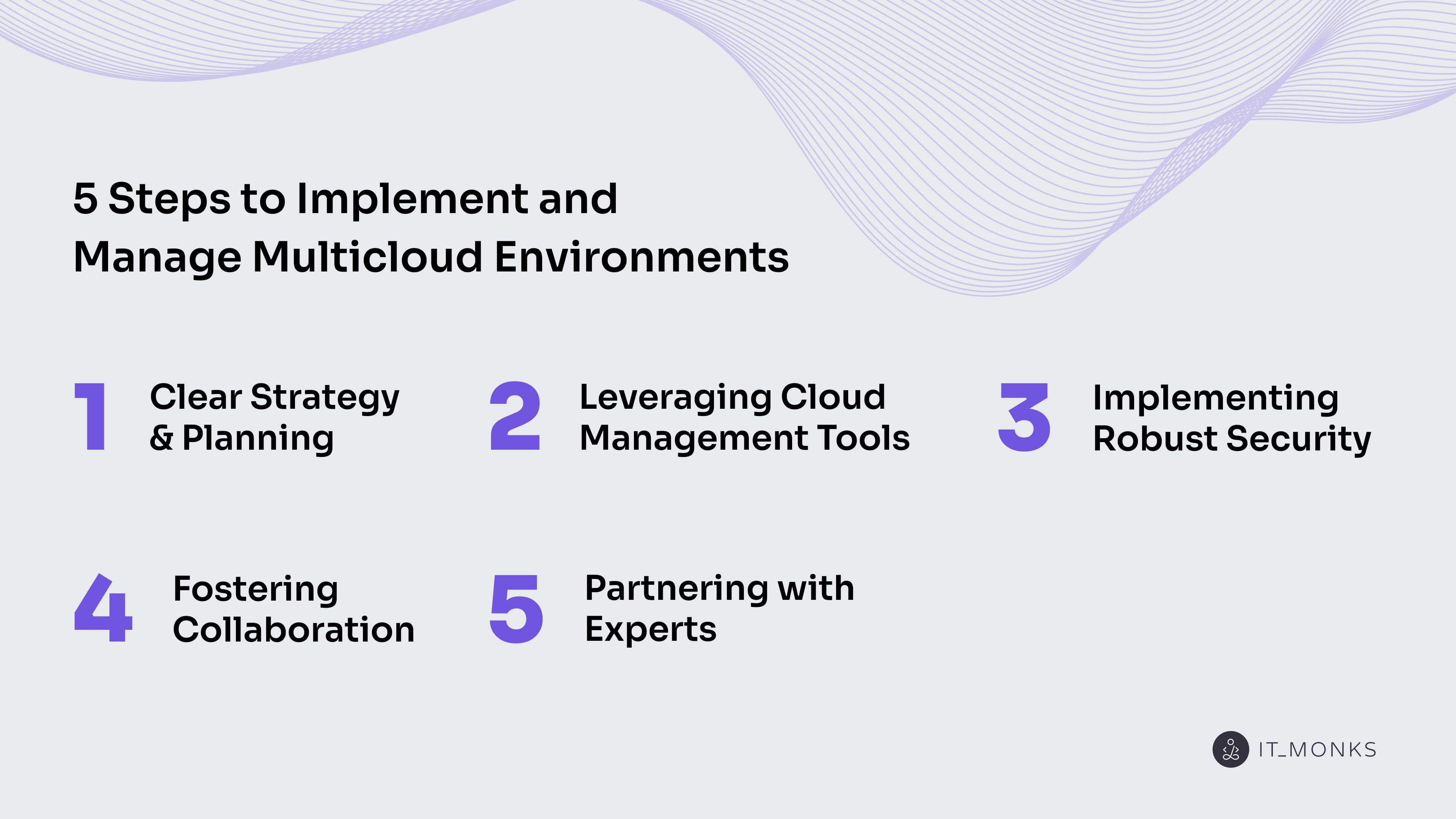
Successfully adopting and managing a multicloud environment requires a well-defined approach, which includes the following five steps:
- Define a clear plan and strategy.
- Utilize cloud management platforms and tools.
- Establish strong security measures.
- Promote teamwork and communication across departments.
- Collaborate with specialized consultants and experts.
1. Clear Strategy and Planning
Clear strategy and planning are the essential first steps in implementing a multicloud environment because they lay the foundation for all subsequent actions.
This phase involves defining goals to align the multicloud approach with overall business objectives, determining workload distribution to decide which applications and data belong on which cloud platforms, and considering business requirements such as compliance, cost, and performance.
2. Leveraging Cloud Management Tools
Cloud management tools provide centralized visibility, automation, and control, helping enterprises manage complexity, reduce operational overhead, and ensure consistent policies across their multicloud deployments.
Some widely used cloud management tools include:
- VMware vRealize: A cloud management platform that enables automation, performance monitoring, and cost management across hybrid and multicloud environments, helping organizations deliver infrastructure and applications faster.
- HashiCorp Terraform: An infrastructure-as-code tool that automates the provisioning and management of cloud resources across multiple providers, making it easier to orchestrate complex multicloud deployments with consistent configurations.
- Microsoft Azure Arc: A management service that extends Azure’s control plane to on-premises, multicloud, and edge environments, enabling unified governance, security, and compliance across diverse infrastructure.
3. Implementing Robust Security
Implementing robust security is vital in a multicloud environment to protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain compliance across diverse platforms. To achieve this, enterprises should enforce strong encryption for data both at rest and in transit, ensure secure APIs to protect communication between services, and implement comprehensive identity and access management (IAM) to control who can access what resources.
Regular security assessments are necessary to identify vulnerabilities and respond to emerging threats promptly. Additionally, adopting a Zero Trust approach, which assumes no user or device is inherently trusted and requires continuous verification, strengthens security by minimizing risks in complex multicloud setups.
4. Fostering Collaboration
Fostering collaboration is essential for enterprises to ensure smooth coordination between IT teams, developers, and business units when managing a multicloud environment. Effective communication helps align cloud strategies with organizational goals, accelerates problem-solving, and reduces silos that can lead to inefficiencies or security gaps.
5. Partnering with Experts
Partnering with experts is crucial for enterprises to successfully set up, optimize, and maintain a multicloud system. Experienced consultants and service providers bring deep knowledge of multicloud architectures, best practices, and emerging technologies, helping organizations avoid common pitfalls and accelerate deployment.
Their expertise ensures that multicloud environments are efficiently configured, secure, and scalable, while ongoing support helps address challenges, optimize performance, and adapt to evolving business needs. Collaborating with enterprise experts allows companies to fully leverage the benefits of multicloud without overburdening internal teams.
Why is it Important to Implement Multicloud?
Implementing multicloud is becoming essential for enterprises as it enables greater agility, scalability, and resilience. For enterprises, adopting a multicloud environment means they can leverage the strengths of multiple cloud providers to meet diverse workload demands, avoid vendor lock-in, and optimize costs and performance.
The importance of multicloud is only set to grow, driven by advancements in cloud-native technologies, AI-powered automation, and more sophisticated integration tools that simplify management across multiple platforms. These innovations make multicloud not just a strategy but a fundamental component of modern enterprise IT infrastructure, helping organizations stay competitive and responsive to changing business needs.
Contact

Send a Project Brief
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from X. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information