What Is the Backend of a Website & How Does WordPress Backend Work?
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
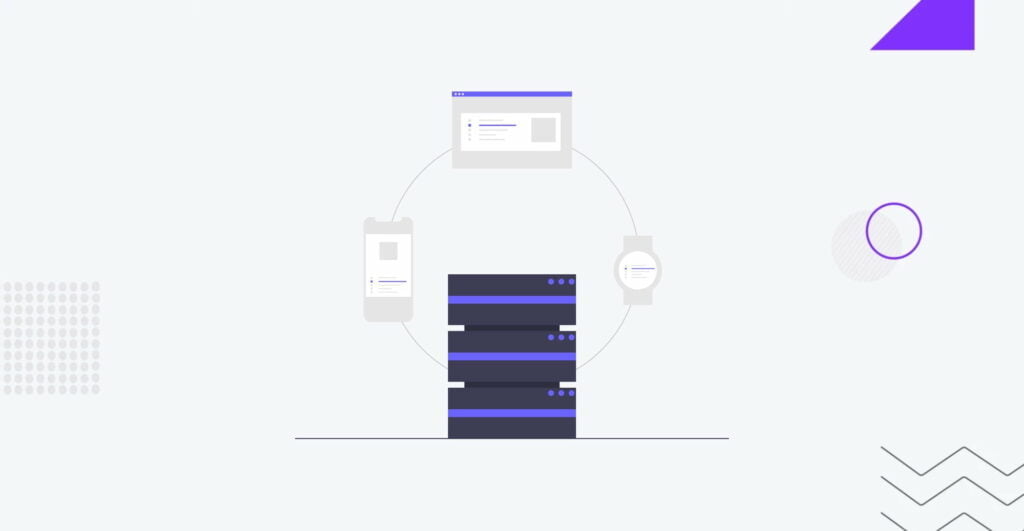
The backendBackendThe server-side of an application responsible for managing data, business logic, and interacting with databases.
More About Backend of a website is the central hub that allows you to handle content, users, settings, and plugins. With this interface, you can effortlessly add new posts and pages, alter the theme, and tweak your site’s settings to suit your preferences. In WordPressWordPressOpen-source content management system (CMS) that allows users to create and manage websites and blogs.
More About WordPress, the “backend” refers to the administrative area or the “dashboard” where website administrators and content creators manage the site’s settings, content, and functionalities. WordPress backend is primarily built using PHPPHPHypertext Preprocessor is a programming language primarily used for web development.
More About PHP, which handles various administrative interface and website management aspects. So, how does the backend of a website work? How to access the WordPress backend to edit code and make the necessary changes for your project? Let’s discuss.
What is the Backend of a Website?
The WordPress backend is accessible to authenticated users, specifically registered users. By default, WordPress does not provide a way to restrict access to the backend of a website, but it offers user roles for this purpose.
User roles are specific categories assigned to registered users on your website, each with its capabilities. The administrator role is the most powerful and should typically be reserved for the website owner. On the other hand, other users should usually be assigned a role that grants them only the necessary permissions. For instance, if a user needs to write, edit, and publish posts but should not have the ability to modify themes or update plugins, an author profile would suffice.
Each WordPress backend section has a specific URL associated with a PHP file. For example, the media library can be accessed through /wp-admin/uploads.php, and user management can be accessed through /wp-admin/users.php. However, there are three different cases.
Posts, pages, and custom post types are handled by the PHP file /wp-admin/edits.php, with the post_type parameter being the distinguishing factor.
Taxonomies like tags and categories are managed by the /wp-admin/edit-tags.php file, with unique taxonomy parameters. Plugins or themes may have unique URLs, such as /wp-admin/admin.php.
The list of backend sections is presented as a menu on the left side of the backend interface. Some sections may also be listed on the top admin bar, and some menus may have submenus. Every section has specific capabilities assigned to it. If a user has the necessary capabilities, they can access the section.
Backend Languages Used in WordPress
Backend languages facilitate communication between applications, servers, and databases. Developers specializing in backend technologies such as Ruby, PythonPythonA high-level, interpreted programming language known for its readability, simplicity, and vast range of libraries and frameworks, making it powerful for various applications.
More About Python, Java, PHP, and .Net, acquire the skills to create server-side applications. These languages effectively manage popular databaseDatabaseAn organized collection of data, typically stored electronically.
More About Database systems like SQLSQLStructured Query Language is a programming language used to manage and manipulate relational databases.
More About SQL, Oracle, and MySQL, which are responsible for storing and organizing website data.
Speaking of backend languages, WordPress and its themes and plugins are written in PHP.
How to Access WordPress Backend
The backend of a website refers to its configuration area. In WordPress, the backend is responsible for the website’s admin area, where you can create or edit content, install plugins, manage design settings, and perform various other tasks. The backend of WordPress is also known as the WordPress admin area or wp-admin.
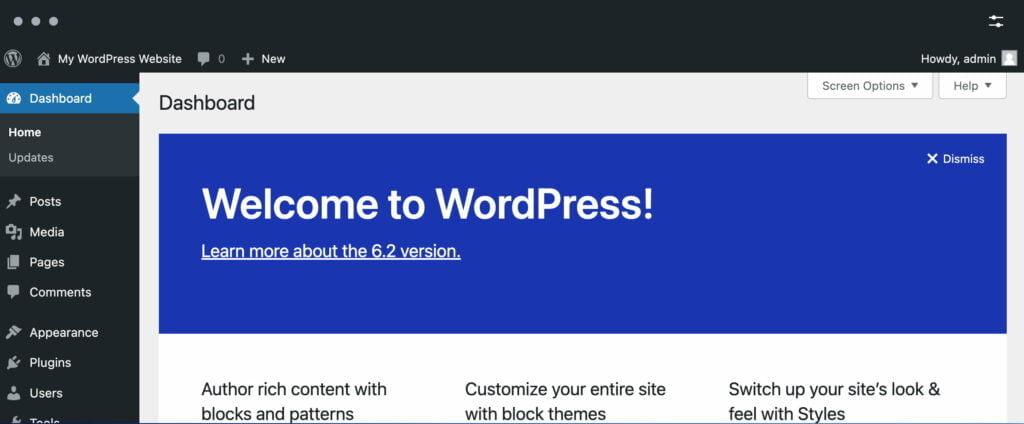
The URL www.yourdomain.com/wp-admin can be used to access the backend in WordPress. By default, the WordPress backend includes various sections. These sections include:
- “Posts” is a section where you can find all articles published on your website. This is where you can create new posts, edit or delete the already published articles.
- “Media” is a section where you can upload and manage media files in your website’s backend.
- “Pages” is where you can create/edit/delete all static pages of your website.
- The “Comments ” section lists all comments published on your website. You can edit, delete, mark as spam, approve, or deny comments.
- “Appearance” is a section where you manage your website’s themes, menus, and widgets.
- “Plugins” tab features external modules/plugins you can install and activate on your website.
- “Users” refers to people accessing your website’s admin area. You can add new users, change their roles, and delete users whenever needed.
- “Tools” is a page where you can import or export content and manage personal data.
- “Settings” is a section where you can manage your website’s global settings.
Depending on the themes and plugins installed on your website, there can be a slight difference in the names of sections.
WordPress Backend Customization
WordPress users greatly value the platform’s flexibility, as it allows for extensive customization of various elements on a website. However, one area that often remains unchanged is the backend of a website. While most businesses focus on modifying the site’s front endFront EndThe visible interface visitors engage with upon visiting a website constitutes its front end.
More About Front End, they often overlook the WordPress admin area.
At IT Monks, our approach is different. Our web development company not only creates websites with a smooth front-end experience for users but also prioritize building a fully functional and user-friendly backend for content creators. We aim to simplify your life, allowing you to concentrate on posting content rather than dealing with code.
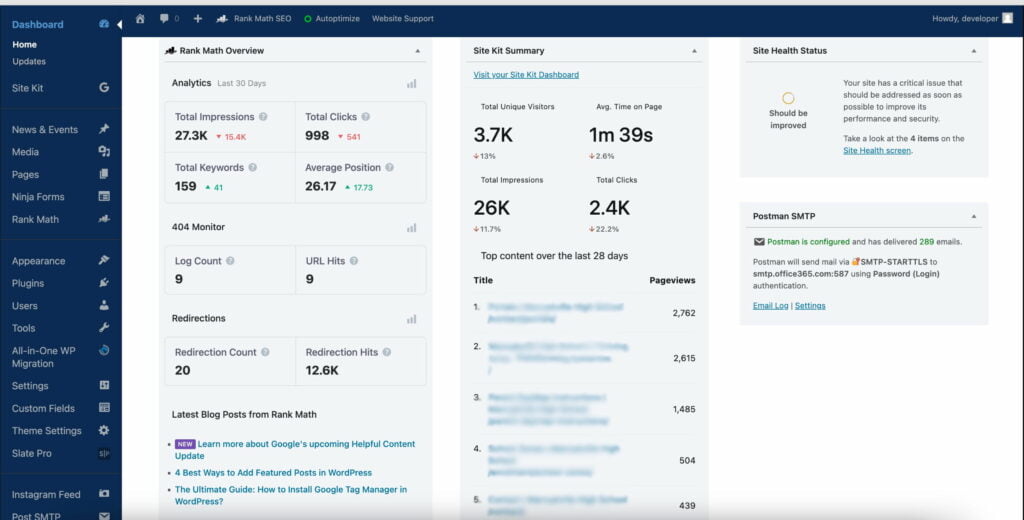
The backend of a website can be designed like this:
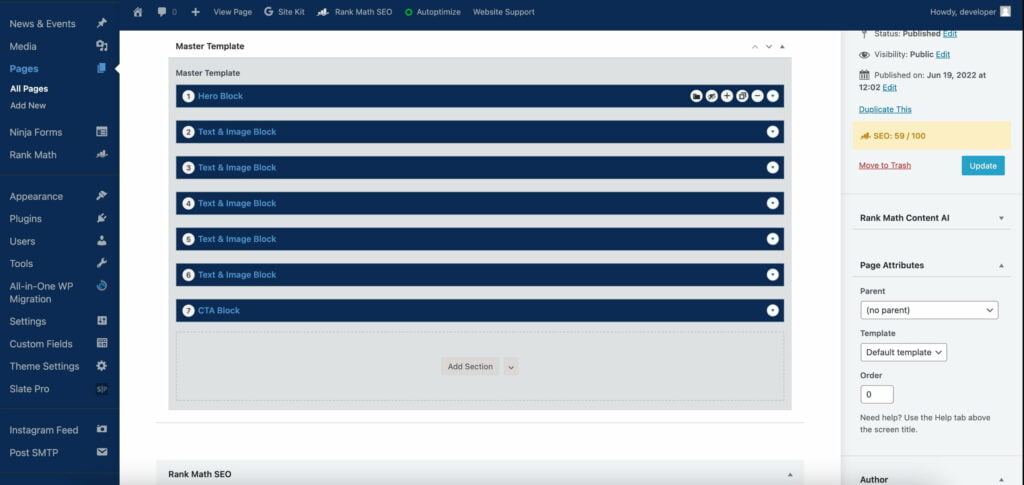
… or like this:
Whether it’s simplifying the interface, adding branding, or making the admin area safer – IT Monks is always willing to create your custom WordPress backend.
How to Write WordPress Backend Code
Please note that editing PHP code in WordPress should be approached with caution. Making mistakes in PHP syntax can cause your website to go down until the original file is restored. Additionally, it is important to consider that plugins are usually available for various customizations on your website, such as adding tracking code to the headerHeaderA visual and typographical band or menu commonly situated at the uppermost part of a website’s interface.
More About Header or creating custom post types. Therefore, we advise exploring alternative options before modifying the PHP code.
When we install WordPress, it automatically generates PHP files that serve as the platform’s backbone. By making changes in these PHP code files, we can effectively manage the backend of WordPress. If you want to write backend code in WordPress, you can do so through the WordPress dashboard. Simply navigate to Appearance >> Theme File EditorEditorThe interface that allows you to write and format text, add images, embed media, and much more.
More About Editor. You will find all the theme code files on the right side. Choose the file in which you want to make changes and start writing your code.
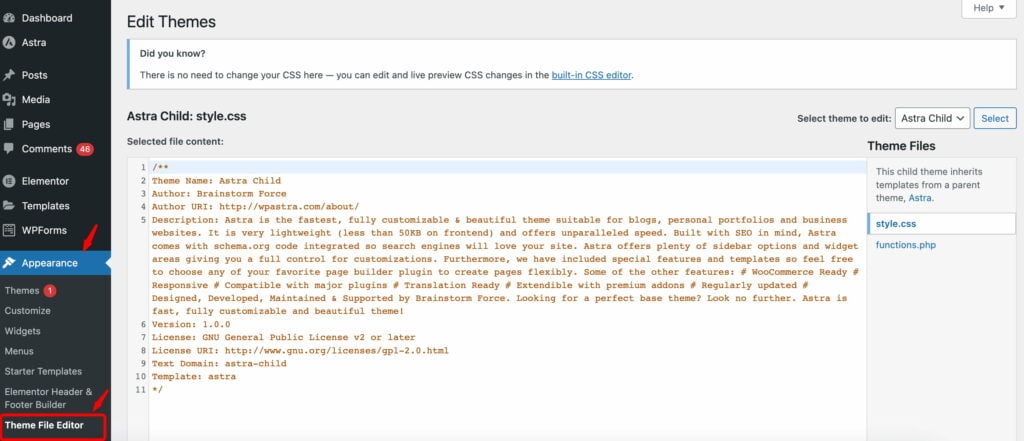
If you install multiple themes or use an adult/child theme combination, you can easily switch between themes in the Editor. The files available for editing will vary depending on your theme. Still, you should at least see the style.css file containing design-related characteristics and the functions.php file, which allows you to adjust WordPress’ default features.
Remember to save your changes by clicking the Update File button after editing your WordPress source code in the Theme Editor.
Final Words
We hope this article has given you a clear idea about WordPress backend, its structure and customization opportunities. The backend of a website is its core section that deserves your special attention.WordPress backend is the place where you can handle content, users, settings, plugins, and write code whenever needed. The latter, in particular, should be approached with caution, since a minor typo can hurt your website a lot.
On top of that, the backend of your website is the section that can be updated with a custom look and feel. If you feel it’s time to update your WordPress website’s backend with a branded style, our web development company is ready to help.



