What is Gutenberg?
Table of Contents
The WordPress block editor – the Gutenberg editor – has officially become an integral part of WordPress core. This significant development begs the question – what implications will this novel approach to WordPress editing have for you, mainly if you already use a WordPress page builder? If you wonder, “What is Gutenberg?” – fear not! This article will guide you through the basics and demonstrate how the block editor works.
A Bit of History
Let’s begin discussing what Gutenberg is with some historical facts about the new WordPress editor.
In December 2018, WordPress 5.0 introduced the inclusion of Gutenberg as part of its core editing functionality. Since then, all the latest WordPress versions feature Gutenberg as the default content editor, which gets more powerful with the new functionality release.
Before WordPress 5.0, WordPress’s default edit screen was perceived as old-fashioned, making agencies and developers worldwide create innovative alternatives for website administrators to update their content without using the default edit screen. These alternatives ranged from static page sections featuring pre-designed content, such as Advanced Custom Fields, to drag-and-drop page builder tools like Beaver Builder.
Despite the numerous advancements introduced by individuals and brands worldwide, the core version of WordPress needed to be improved. For instance, without coding expertise, users found it challenging to insert an image next to a text block without disturbing the entire layout.
As a result, the community of developers and designers who maintain the WordPress platform dedicated their time and expertise to creating a new and improved editor – Gutenberg – to enhance the editing experience.
What is Gutenberg editor in WordPress?
Gutenberg, a block-based editor, was unveiled for the WordPress platform alongside the release of WordPress 5.0. Since then, numerous website owners have transitioned from the classic editor to Gutenberg, and it has become the default editor for WordPress installations.
The Gutenberg WordPress editor distinguishes itself from its predecessor – now called the “classic editor” or “TinyMCE editor” – through its innovative block-based approach to content creation.
Gutenberg treats every element in your content, such as a paragraph, image, or button, as a block. This approach enables seamless content manipulation and offers immense flexibility to users.
Moreover, third-party developers can develop custom blocks, eliminating WordPress’s reliance on shortcodes. For instance, users can effortlessly add their form plugin‘s block instead of using shortcodes like [your-form-shortcode] to embed a contact form, as was done previously.
Beyond this, users can employ blocks to craft intricate layouts, such as setting up multi-column designs or grouping blocks to create a coherent section.
As we further illustrate how to use the block editor, you will discover various ways to leverage blocks to enhance your content creation experience.
Who is Gutenberg?

Before diving into more details on the WordPress Gutenberg editor, let’s find out “Who is Gutenberg?”
In approximately 1450, a daring and ingenious man named Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg developed the world’s inaugural printing press in Germany. Driven by a genuine desire to disseminate the Bible to those lacking access, Gutenberg refused to accept the status quo. At that time, only priests had permission to read the Bible to their congregations, and some of them interpreted it in a manner that served their agenda.
Gutenberg, however, believed in something grander and more inclusive and was willing to risk everything to realize his vision. As a result, the Gutenberg Bible came into being. Although it may not be as dramatic as putting one’s life on the line, the WordPress Gutenberg editor’s ethos is similar: democratizing publishing and granting the masses access to content creation rather than reserving it solely for the marketing elite.
Gutenberg’s printing press was a symbol of freedom. Before its invention, only priests could read and interpret the Bible for the masses. But with the printing press, the Bible became accessible to everyone, and people could finally read and interpret it for themselves.
This is similar to the shift in website platforms, with WordPress and the Gutenberg editor leading the charge. Previously, only those who could afford expensive license fees and had the technical skills to develop a content management system could create and manage content effectively.
However, the Gutenberg editor has changed this by making content creation and management accessible to regular users. Just as the printing press democratized access to information, the Gutenberg editor has democratized access to website management and content creation, leveling the playing field for all. And the best part? It’s free and open-source.
In short, the Gutenberg editor has the same values as Gutenberg’s printing press: freedom, accessibility, and empowerment.
Who Is New WordPress Editor Intended For?
Gutenberg is a powerful tool that can benefit everyone, but let’s examine the advantages for different types of users.
Enterprise
Gutenberg has made managing content easier for enterprise brands without relying on a development team. Launching a blog or creating a unique Gutenberg theme can provide a flexible experience that can be rolled out across multiple websites and brands. If something needs to be updated, it’s as simple as replacing or introducing new blocks rather than developing the theme from scratch.
This level of flexibility is precious for enterprise brands, which are often viewed as rigid and inflexible. Gutenberg allows businesses to be agile and adapt to changing market demands quickly. Making WordPress for Enterprise even more beneficial.
Marketers
Marketers dream of controlling their websites and content creation without relying on developers or external agencies. Gutenberg provides a significant advantage to marketers and content writers by allowing them to quickly produce, check, and publish content.
One of Google’s primary ranking factors is relevance, meaning content should be relevant to a user’s initial search or interests. With Gutenberg, marketers can create relevant content quickly and publish it when it matters most. If there’s breaking news relevant to a brand, they can create, check, and publish content within minutes.
Small Businesses
Platforms like Squarespace and Wix have dominated the market regarding ease of use for small businesses, but the result often needs to be better. Building a website on these platforms still requires a significant effort to create something worthwhile.
In the past, building a website with WordPress was a challenging experience. Gutenberg has made this process significantly easier by providing a flexible way to lay out pages, posts, and other content using blocks. With WordPress, thousands of themes are available, allowing business owners and employees to download and install a theme that suits their brand.
End Users
Ultimately, the success of a website depends on the end user. Gutenberg has revolutionized website design and development by making better, more relevant content manageable. The user experience has also improved, thanks to dynamic blocks that help users flow from one page to the next.
For example, service pages can contain relevant blog posts, or team member profiles can link to case studies or news articles. Gutenberg’s flexible block system allows endless possibilities, providing users with relevant content that meets their needs.
Gutenberg is a game-changer for website design and development. It benefits enterprise brands by providing flexibility and agility, marketers by allowing for quick and relevant content creation, small businesses by making website building easier, and end users by providing a better experience.
Gutenberg Editor vs. Classic Editor
Regarding content creation in WordPress, two editors are available: the Classic Editor and the Gutenberg Editor. While both serve the same purpose, there are some noticeable differences between the two.
One major difference is the editor interface. The Classic Editor provides a simple text editor similar to Microsoft Word. In contrast, the Gutenberg WordPress block editor has a responsive and user-friendly interface with self-explanatory icons that are easily accessible.
The Classic Editor provides a blank canvas for writing posts and pages regarding content creation. In contrast, the Gutenberg WordPress block editor has a broader range of features for creating content and managing its visual aspects more efficiently.
Another significant difference is the ease of use. The Classic Editor requires basic HTML knowledge to utilize all its possibilities, while the newer tool does not require technical expertise. Instead, users can drag and drop blocks to create pages and posts.
The Classic Editor has basic formatting features for site editing but lacks design flexibility. It’s not the best choice for creating media-rich pages or complex layouts. The new WordPress editor includes features such as reusable blocks for creating templates.
How to Switch to Block Editor in WordPress?
In case you are currently editing a Page or Post that is still utilizing the Classic Editor and you want to switch to the Block Editor, you can do so by following these simple steps:
Step 1: Navigate to your website’s Dashboard.
Step 2: On the left-hand vertical menu, click on either Pages or Posts.
Step 3: Choose the page or post you wish to switch to the Block Editor.
Step 4: On the right-hand column, search for the link labeled “Switch to block editor” and click on it.
Navigating Gutenberg
Gutenberg is an editor for WordPress that utilizes blocks to help users create content quickly and efficiently. Using blocks, users can concentrate on generating content without worrying about the layout, as they can easily rearrange the blocks by dragging and dropping them.
Now, let’s explore how to navigate Gutenberg in your WordPress dashboard.
Step 1. Sign in to your WordPress dashboard.
Step 2. Click on Posts or Pages.
Step 3. Click “Add New.”
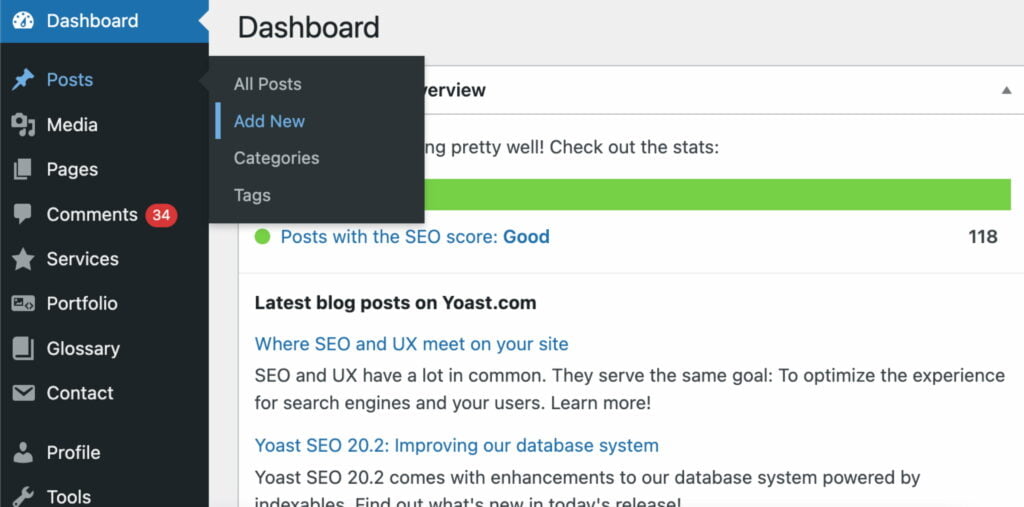
Step 4. The screen that appears in front of you is the Gutenberg editor. You will use the Gutenberg block editor by default whenever you create a new post/page or click to edit the existing one.
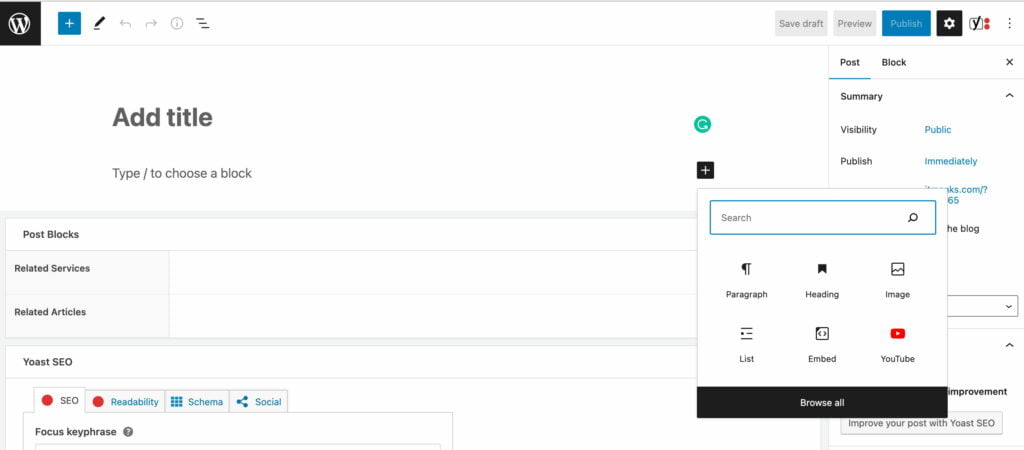
Top Bar of the Gutenberg Editor
On the top left corner of the screen, you will find several options, including “Add a block,” “Undo/Redo,” “Content structure,” and “Block navigation.”
On the top right corner, you will find links and buttons for various options, including “Save Draft,” “Preview,” “Publish,” “Show/hide settings,” and “Further tools and options.” Here’s a visual representation of these options:

Content Section
In the Gutenberg editor, content is organized in the form of blocks. The first block is always reserved for the title. In the screenshot provided, each highlighted section represents a separate block. When you hover over a block, various options related to that block will appear, as shown in the image below.
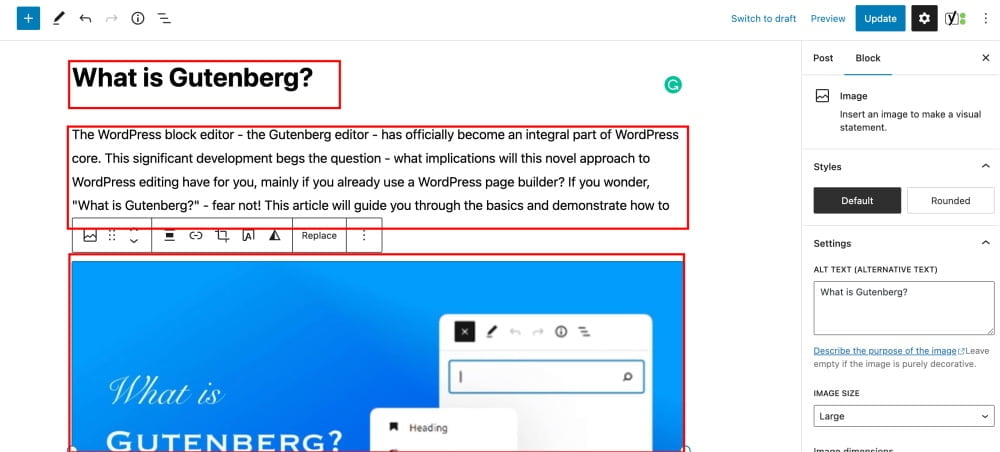
Options Column
Furthermore, note the sidebar on the right-hand side of the screen when you select a block. Each block you choose will be associated with the options displayed in the sidebar. The sidebar presents diverse details that can be modified within the selected block.
For instance, if you choose an image block (like shown in the image above), you can adjust various settings such as styles, alt text, image size, image dimensions, and advanced settings. To toggle the sidebar’s display, click on the gear icon in the top right-hand corner.
How the Gutenberg Editor Works
As the name of the Gutenberg Block Editor suggests, it allows you to create content using individual blocks. These blocks are diverse and offer multiple options, which can be accessed by clicking on the plus icon in the page’s top-left corner or within the page’s body.
You can add simple paragraph or image blocks and more complex blocks such as lists, galleries, and tables. The possibilities are endless.
Once you have selected a block, it will be inserted into your post or page. You can then click on it to access the toolbar settings and customize it to your liking. Further customization options can be found on the right-hand sidebar.

Suppose you’re working with a Paragraph block. In that case, you can create an anchor link, modify the text’s color and typography, and perform other customizations. Each content piece can be added as a block, adjusted with the settings provided, and organized in your preferred order on the page.
Additionally, the new WordPress editor lets you work with pre-designed patterns. To access the Patterns option, click on the “+” icon in the top left corner of the Gutenberg editor dashboard, and you will see a sidebar with the Blocks and Patterns tabs.
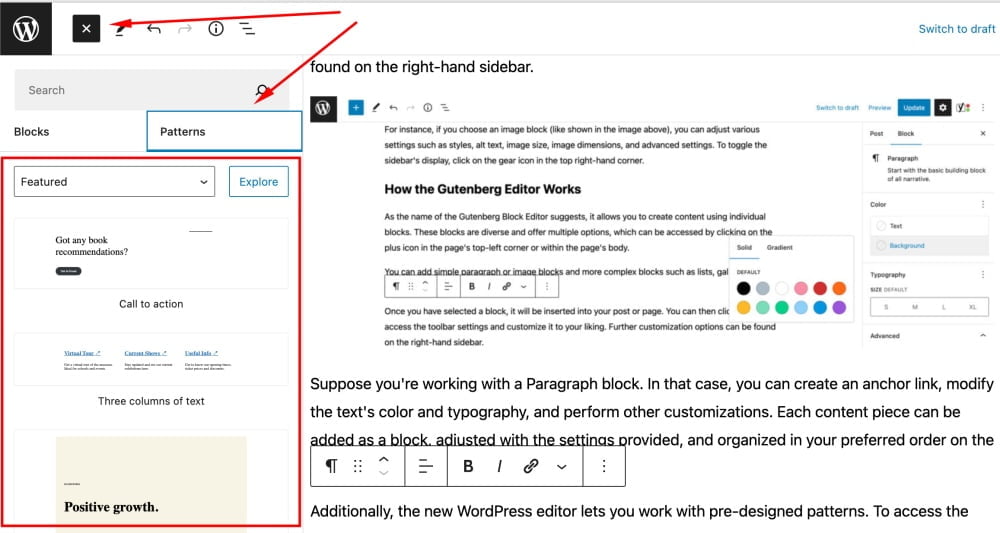
The Gutenberg Block Editor offers pre-designed layouts for headers, galleries, and other elements you can personalize according to your requirements. You can also save your customized elements as reusable blocks, which you can effortlessly add to other posts and pages.
You can click on any pre-designed pattern, and it willl be added to your post or page as is. Then, you can proceed editing content by clicking on the pattern’s elements, like headings, buttons, visuals, etc.
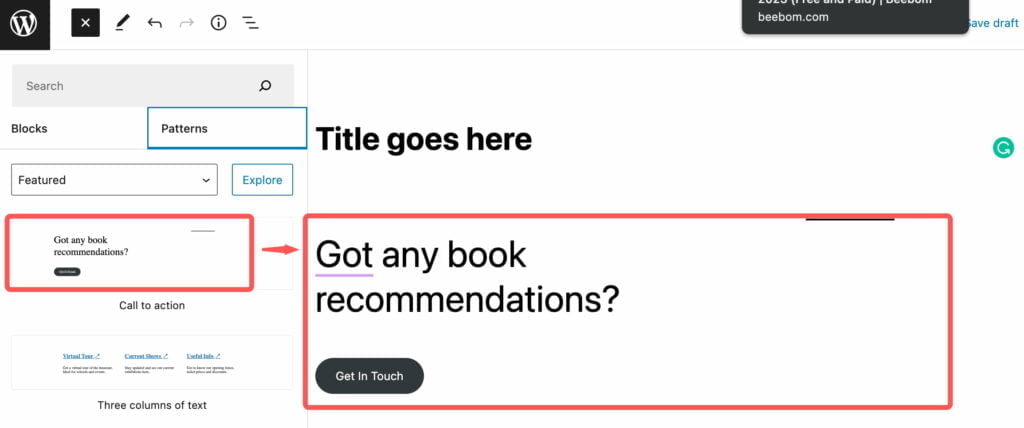
How to Create a New Gutenberg Block
Now, let’s discuss how to work with Gutenberg blocks in more detail. First, let’s see how to add a new block to your post or page.
A title is the first block to be added to every post or page.
1. Click on the Block Inserter+ icon on the top toolbar.
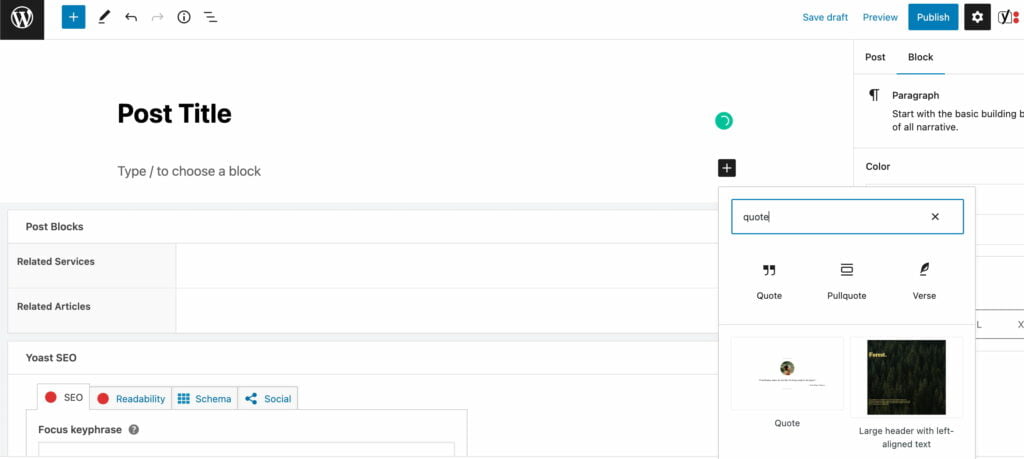
2. Choose the block you’d like to add after the title. As a rule, that’s an image or a paragraph block that comes after the title. In this tutorial, let’s see how to add the Quote block to your blog post.
3. To include additional blocks below the quote, click on the + icon, as shown below. Mind that whenever you press Enter, the WordPress block editor will automatically generate a new paragraph block.
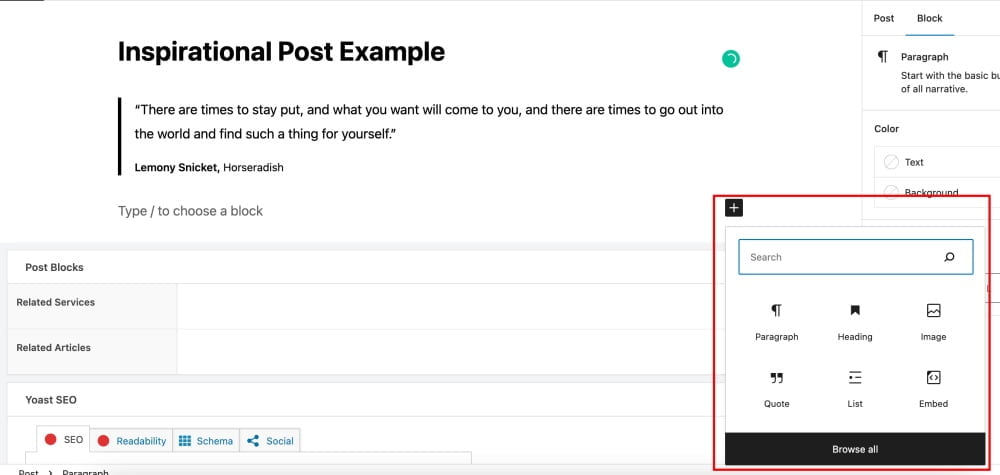
4. Clicking on the “+” icon, you will see the panel showing the most frequently used blocks. You can search for a specific block using the search bar or clicking “Browse All.”
How to Customize Gutenberg Blocks
Gutenberg editor allows you to adjust all blocks to fit your preferences using the built-in customization settings and build custom blocks.
Here is how to customize Gutenberg blocks.
1. Click the “+” icon on the top toolbar to access the Block Inserter interface.
2. Select the block you want to customize. For example, you can choose the Buttons block.
3. The block settings will appear once you’ve added the button block. Alternatively, you can click on the “Settings” button on the top-right corner of the editor to load the Sidebar panel.
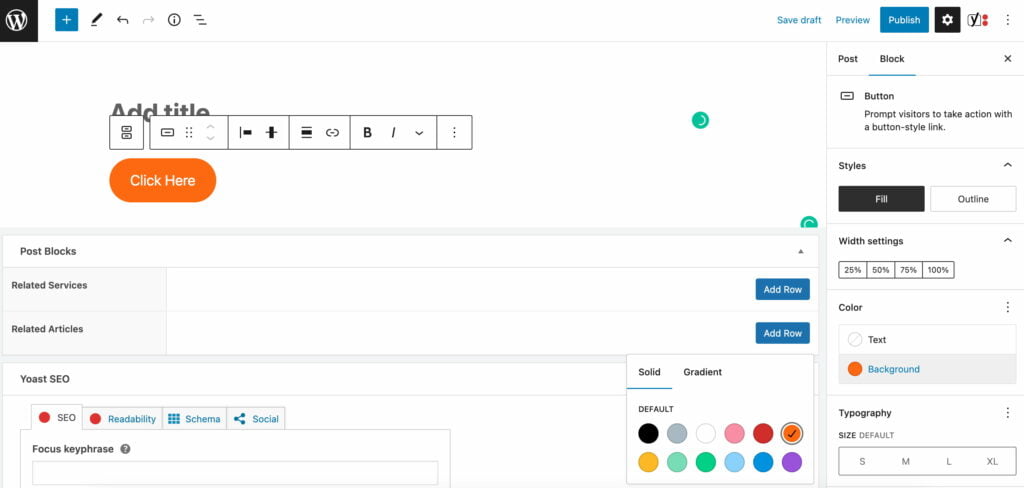
4. Within the Block settings, you can style the button using either Fill or Outline.
5. You can also adjust the Width Settings, which range from 25% to 100%.
6. To change the button’s text and background color scheme, navigate to the Color section.
7. In the Typography settings, you can select either the default button size options or custom sizes to determine the button size.
8. Using the Border settings, you can adjust the button’s border by toggling the dot.
9. Lastly, at the bottom of the Sidebar, you’ll find the Advanced section, which allows you to add Link rel, HTML anchor, and Additional CSS class(es) for further customization.
Content Structure in Gutenberg
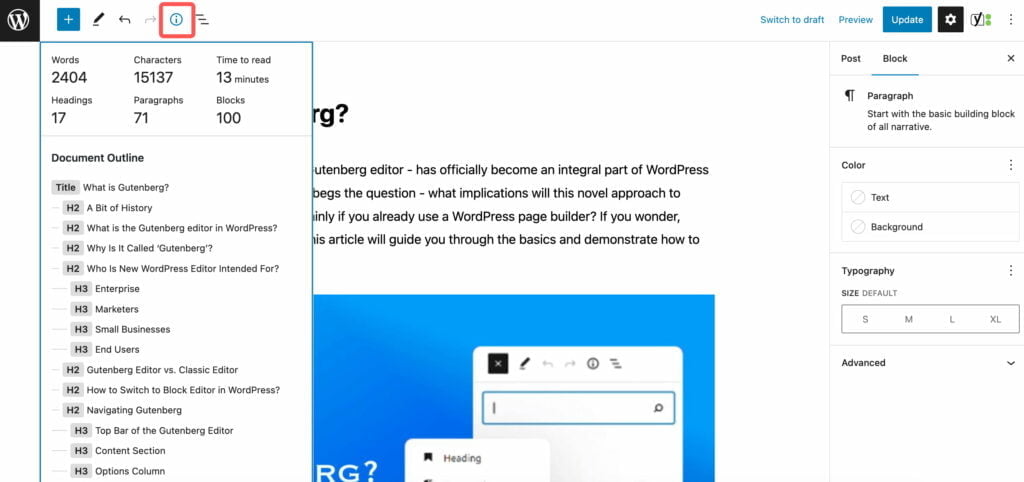
Having information about the structure of your page or post can be quite valuable. It provides a quick overview of the length and format of your content. Additionally, by utilizing titles and headings, you can create a helpful outline of your content. This is particularly useful when dealing with longer pieces, as it allows readers to easily navigate and jump to different sections of your post or page.
You can check the content structure of your blog post or website page by clickinhg on the “i” icon in the top left corner of the page. You can see the content structure information. Clicking on any item within the content structure pop-up, you’ll be taken to that section in your post.
WP Gutenberg Pros & Cons
If you are still with the Classic Editor, you may wonder if switching to Gutenberg is worth it. If you are new to both options, we recommend Gutenberg block editor as a better option for seamless seamless content creation and editing experience.
Gutenberg Pros
- Gutenberg is an intuitive content creation tool that simplifies the process, making it easier for beginners to get started. One of the key advantages of Gutenberg is that it allows you to preview your content in a format that closely resembles the final output on the front end. This means you can easily visualize the result and make necessary adjustments before publishing.
- Another benefit of Gutenberg is that it unifies the content creation experience by eliminating the need for separate shortcodes. Shortcodes can confuse new users and make the editing process more complex. Gutenberg streamlines the editing process by providing a user-friendly interface incorporating various discrete elements and making it more accessible for users at all levels.
- In addition, Gutenberg provides more options for customizing your content through various elements, including blocks, widgets, and plugins. These discrete elements allow you to easily add functionality and customize your content without advanced coding knowledge.
- Gutenberg eliminates the need for a separate page builder plugin. This means that you can create and edit content without relying on third-party tools, which can save time and streamline your workflow.
- Gutenberg offers a range of benefits for content creators of all levels, making it a valuable tool for anyone looking to create high-quality content with ease.
Gutenberg Cons
- While Gutenberg aims to offer an intuitive interface, it can be challenging to learn compared to the Classic Editor. Gutenberg offers a broader range of options and settings, which can overwhelm new users and make editing more complex.
- Another potential disadvantage of Gutenberg is that switching from the Classic Editor to the Block editor may break your site. You may have to manually redesign each post and page using Gutenberg, which can be time-consuming and frustrating.
Conclusion
The answer to the question, “What is Gutenberg” is simpler than you could have imagined. Gutenberg is a user-friendly WordPress editor that allows users to create pages and posts using blocks. This editor is now the default option for WordPress, with the Classic Editor no longer receiving support from the WordPress team.
It’s important for WordPress users to familiarize themselves with the Block Editor and take advantage of its many features. By doing so, you can streamline your content creation process and create high-quality content with ease.
Overall, Gutenberg represents a significant step forward in WordPress editing, offering a more intuitive and flexible interface for content creators of all skill levels.
Contact
Don't like forms?
Shoot us an email at [email protected]
Send a Project Brief
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Turnstile. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from X. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information



