Enterprise Website Relaunch
Table of Contents
An enterprise website relaunch is a significant overhaul of an existing large-scale business website, aimed at improving performance, refining content, enhancing information architecture, ensuring accessibility compliance, redesigning, selecting a CMS that supports business needs, setting up the technology stack, and optimizing SEO.
The primary purpose of a relaunch is to improve user experience, expand functionality, refresh brand identity, increase search visibility, achieve business objectives, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
This process may also be necessary if the existing site is outdated, underperforms on mobile devices, or faces technical issues that hinder its success.
To ensure the relaunch is effective, it requires careful planning and strategic alignment with the business’s goals, timeline and budget. A thorough website audit should be conducted before starting, to assess the strengths and weaknesses of the current site.
The relaunch must be driven by the business’s objectives, ensuring it aligns with both short-term needs and long-term visions.
Additionally, the design must complement the company’s brand identity, provide excellent accessibility for all users, and prioritize security to protect user data and business assets.
A successful relaunch also requires thorough quality assurance (QA) testing to ensure the website functions properly across all devices and browsers.
Post-launch monitoring and ongoing maintenance are essential to continuously track, maintain, and enhance the website’s performance, security, and functionality, addressing issues promptly and ensuring the site remains operational and optimized over time.
What is Enterprise Website Relaunch?
An enterprise website relaunch is an overhaul of a large organization’s existing website, involving a complete modernization of its design, content, functionality, and underlying technology. This process involves major changes — from design and site architecture to functionality and content.
The relaunch of an enterprise website aims to improve performance, enhance user experience, and stay competitive in a digital-first market. In many cases, it also includes technical improvements, such as a faster backend, mobile responsiveness, or tighter integrations with third-party tools.
The goal is to create a more effective, modern, and user-friendly platform that better reflects the organization’s evolving identity and meets business objectives.
What is the Purpose of an Enterprise Website Relaunch?
The purpose of an enterprise website relaunch is to enhance usability, advance capabilities, revitalize brand presence, boost search performance, drive business outcomes, and sustain market relevance.
- Enhancing Usability. When users struggle to find information or navigate the site efficiently, engagement and satisfaction drop. A site relaunch solves this by improving the overall user experience, from simplifying navigation and optimizing layouts for mobile to making the site accessible to all.
- Advancing Capabilities. As business models evolve, legacy websites often lack the technical infrastructure to support new demands. A relaunch website initiative allows for integrating advanced features, such as personalization engines, multilingual support, or CRM tools, that improve performance and better serve user needs.
- Revitalizing Brand Presence. A website that looks outdated or inconsistent with brand messaging can weaken trust. Through a design relaunch, companies can refresh visuals, tone, and storytelling to align with their current identity and vision, making the website a more effective brand ambassador.
- Boosting Search Performance. A poorly optimized site can limit visibility in search engines, leading to lost opportunities. An SEO website relaunch addresses this by improving technical SEO, reworking site architecture, and aligning content with strategic keywords. The result is stronger organic traffic and better positioning in search results.
- Driving Business Outcomes. An ineffective website can slow down lead generation and hinder conversions. With a website relaunch, businesses can refine user journeys, add persuasive calls-to-action, and optimize performance — all of which contribute to increased revenue and measurable ROI.
- Sustaining Market Relevance. Stagnant websites quickly fall behind competitors. A website refresh helps keep up with digital trends and audience expectations, ensuring that the platform remains compelling and competitive in a constantly shifting online landscape.
Regardless of the motivation, every enterprise web relaunch should be grounded in a clear, well-structured plan. Without it, even the most ambitious efforts risk failing. Careful preparation — from strategy and design to SEO and analytics — turns a relaunch guide into a roadmap for long-term success.
Business Goals Alignment
The success of an enterprise website relaunch heavily depends on how well it aligns with clearly defined business goals. Without direction, even the most visually appealing relaunch can fall short of delivering real value.
Clear goals structure the entire process. They shape decisions around design, content, technology, and timeline, and keep the internal team and stakeholders focused on what truly matters.
For instance:
- If the goal is to boost brand awareness, the relaunch may focus on visual identity and storytelling.
- If it’s to generate more leads, the site structure and UX will emphasize forms, CTAs, and conversion paths.
- If the aim is to improve customer experience, then intuitive navigation, mobile responsiveness, and accessibility become top priorities.
Each goal influences the direction of the relaunch, from early planning and platform selection to content strategy and feature integration. It also sets the framework for measuring post-launch success.
Clear goals help steak holders stay aligned, reducing back-and-forth and ensuring resources are used effectively. Whether it’s marketing, sales, customer support, or IT, every team benefits from knowing what the relaunch is meant to achieve.
Enterprise Website Audit

Enterprise website audit is an in-depth examination and analysis of a large website, which includes website performance review, technical evaluation, content assessment, and UX and UI review. It helps identify issues in the existing website and informs decisions for the new site, ensuring that the relaunch will improve overall performance, user experience, and business outcomes.
- Performance Review: Analyze page speed, load times, and Core Web Vitals to ensure optimal site performance and speed.
- Technical Evaluation: Assess site health by checking server performance, URL structure, sitemaps, robots.txt, mobile readiness, and security setup.
- Content Assessment: Evaluate content for relevance, accuracy, and SEO optimization and identify gaps or duplicate content.
- UX and UI Review: Assess the user experience by analyzing navigation, design consistency, mobile optimization, and accessibility.
Let’s consider each of these points in more detail.
Performance Review
A performance review is a comprehensive analysis of an enterprise website’s speed, responsiveness, and technical efficiency across different devices, browsers, and user conditions.
This audit ensures that the website delivers a smooth and reliable experience while supporting the brand’s SEO goals, customer engagement, and conversion rates. By diagnosing and addressing performance-related issues, businesses can enhance user satisfaction and maintain a competitive digital presence.
Key areas of focus during a performance review include:
- Page Load Speed: Measuring how fast each page loads and identifying issues like heavy media files, bloated code, or unoptimized scripts that may affect user engagement and SEO.
- Server Performance: Evaluating hosting and server response times to ensure fast data delivery and minimal downtime.
- Mobile Optimization: Confirming that the website runs smoothly on mobile devices, where speed and responsiveness directly impact rankings and usability.
- Core Web Vitals: Reviewing Google’s key performance indicators (LCP, FID, CLS) to ensure the site meets modern expectations for speed and interaction.
- Third-Party Scripts: Auditing the impact of analytics, chat tools, and advertising scripts on overall site performance.
- Browser Compatibility: Verifying consistent functionality across major browsers to avoid issues that could frustrate users or lead to errors.
Technical Evaluation
A technical evaluation is a deep dive into the backend health of an enterprise website, focusing on the foundational elements that power its performance, reliability, and scalability. This audit ensures the site’s infrastructure is secure, stable, and capable of supporting complex system integrations.
By identifying issues in code quality, system configuration, and platform integrations, businesses can prevent downtime, enhance security, and prepare the site for future enhancements.
Key areas of focus during a technical evaluation include:
- Code Quality: Reviewing front-end and back-end code for efficiency, readability, and maintainability, identifying redundant or outdated code that could slow down the site or introduce errors.
- Server & Hosting Environment: Assessing server performance, uptime, and scalability to ensure fast, reliable access to the website under varying traffic loads.
- CMS & Database Health: Checking the content management system and database structure for issues such as slow queries, bloated content tables, or outdated plugins and extensions.
- Security Protocols: Verifying the presence of HTTPS, firewalls, security headers, and protection against vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
- System Integrations: Testing APIs, third-party tools, and platform integrations (e.g., CRMs, ERPs, analytics) for performance, stability, and data accuracy.
- Configuration Files: Reviewing robots.txt, .htaccess, and sitemap.xml for proper setup to support crawlability, performance, and SEO hygiene.
Content Assessment
Content assessment is a review of a website’s content to evaluate its quality, relevance, and alignment with both SEO best practices and business objectives.
This audit analyzes content for accuracy, SEO optimization, user engagement, and its role in achieving the company’s goals. The purpose is to identify areas for improvement, such as outdated or duplicate content, and to uncover opportunities for new content based on keyword research and competitor analysis.
Key focus areas in the content assessment process include:
- Content Quality and Relevance: This focuses on ensuring the content is accurate, credible, and aligns with the website’s purpose. It evaluates content against industry standards and user expectations to provide valuable, up-to-date information that enhances authority and user trust.
- SEO Optimization: SEO optimization involves ensuring content is structured and optimized for search engines. This includes proper keyword usage, meta tags, and on-page elements, aiming to improve search engine visibility and ranking while aligning content with user search intent.
- Duplicate Content and Keyword Cannibalization: This aspect of the audit identifies duplicate pages or content targeting the same keywords. Addressing these issues prevents confusion for search engines, consolidates ranking signals, and ensures that each page targets distinct keywords and search intents to maximize SEO performance.
- Content Strategy Alignment: This ensures content aligns with overall business goals and user needs. It involves identifying content gaps, measuring performance against key metrics, and optimizing calls to action, ensuring content supports conversions and long-term marketing objectives.
UX and UI Review
UX and UI Review is a detailed examination of a website’s user experience (UX) and user interface (UI), aiming to identify pain points, strengths, and areas for web design improvement. This audit focuses on usability, accessibility, and performance to ensure a seamless, engaging, and effective user journey.
The review helps uncover usability challenges, such as difficult navigation or confusing layouts, and provides actionable insights to enhance the website’s functionality. By evaluating factors like content clarity, speed, and brand consistency, the audit identifies opportunities to improve overall user satisfaction and interaction.
The goal is to ensure the website delivers a frictionless and enjoyable experience, driving conversions and fostering customer loyalty.
Key focus areas of the UX/UI audit include:
- Usability: Ensuring ease of navigation and task completion.
- Accessibility: Making sure the site is usable for people with disabilities.
- Interface Design: Analyzing visual appeal, consistency, and responsiveness.
- Information Architecture: Assessing the site’s logical structure and user understanding.
- Content Strategy Alignment: Reviewing how content placement and structure support user flow and business messaging.
- Visual Consistency: Ensuring that UI elements follow a cohesive design system to reinforce brand trust and usability.
Project Timeline Planning
Project timeline planning is a process of strategically mapping out every phase of an enterprise website relaunch, including the redesign and development phase, the testing and launch stage, and the post-launch period.
The process starts with defining clear objectives, such as improving usability or expanding functionality. The scope, budget, and timeline are established, and roles are assigned across the design, development, content, and project management teams.
- During the redesign and development phase, the team creates a strategy with wireframes and user flows, develops the visual design, builds the core functionality, and prepares engaging and SEO-friendly content.
- The testing and launch stage involves reviewing the site’s functionality, usability, and performance through internal QA and beta testing with select users. Once ready, the website is deployed to the live environment.
- In the post-launch stage, user feedback and analytics inform continuous monitoring, maintenance, and performance enhancements.
Project Budget Estimation
Project budget estimation is a process of calculating the total cost required to plan, design, develop, and launch a new enterprise website.
In the context of a website relaunch, this step is critical for aligning expectations, securing stakeholder buy-in, and ensuring the project stays on time and within financial limits. A realistic, well-researched budget prevents scope creep, supports better decision-making, and helps prioritize features and phases based on available resources.
The estimation process typically includes:
- Scoping out project requirements and technical complexity;
- Accounting for team resources;
- Estimating costs of design, development, content work, integrations, and testing;
- Planning for ongoing maintenance, support, and potential contingency reserves.
For enterprise projects, budgeting must also consider legacy systems, third-party services, compliance, and long-term scalability.
Content Strategy

Content strategy is a plan that outlines how to manage and utilize existing content, create new content, and ensure it aligns with the relaunch’s goals and user needs. It serves as a blueprint for how the website will communicate, support business objectives, and deliver value to users.
A strong content strategy helps large organizations avoid carrying over outdated, redundant, or fragmented messaging. It ensures that every piece of content on the new site (like text, images, documents, and metadata) plays a role in informing, converting, or engaging the target audience.
This involves clearly defining audience segments, mapping their content needs at different stages, aligning key messages with business objectives, and coordinating with design and development teams to ensure consistency across the site.
During a relaunch, content strategy is not just about writing new pages, it’s about refining what exists, identifying gaps, and shaping a coherent structure that enhances user experience.
It also ensures content operations are scalable and maintainable after launch.
Two critical steps round out this process: a content audit to evaluate what’s already there and worth keeping, and a smooth migration plan to move valuable assets to the new site without losing performance or SEO value.
Content Audit
A content audit is the process of systematically reviewing and evaluating all existing website content to assess its quality, performance, and alignment with current business goals. It helps determine what to keep, update, consolidate, or remove, ensuring the new website is efficient, user-centric, and strategically sound.
Large organizations often accumulate years’ worth of content, much of which may be outdated, inconsistent, or no longer relevant. Without a thorough audit, this legacy content can clutter the new site, confuse users, dilute brand messaging, and negatively impact SEO performance, all of which reduce the effectiveness of the relaunch.
Content audit contributes to a successful enterprise website relaunch through the following steps:
- Inventory and Categorization. The audit begins with compiling a complete inventory of all existing content —web pages, documents, blog posts, media files, and more.
Each item is then categorized by topic, format, intended audience, and other relevant filters to build a clear picture of the website’s current content landscape. - Performance Analysis. Using analytics tools, you assess how well each piece performs in terms of traffic, engagement, conversions, and SEO metrics.
- Identifying Issues and Opportunities. The audit reveals broken links, duplicated content, inconsistent messaging, and outdated information. It also highlights high-performing assets that can be reused, expanded, or optimized for greater impact.
- Informing the Content Strategy. Audit findings directly shape the new content strategy by clarifying which content should be rewritten, removed, or newly created. It also helps inform the content migration plan — ensuring only purposeful, high-quality materials are moved to the new platform.
- Enhancing User Experience and SEO. By eliminating clutter and improving content quality, the site becomes easier to navigate and more engaging for users. At the same time, better-structured and more relevant content helps boost search engine visibility.
- Streamlining Content Operations. The audit often uncovers process inefficiencies, such as inconsistent publishing workflows or lack of content ownership.
A content audit delivers a clear roadmap for improvements by identifying what to keep, update, or remove. This process shapes content strategy and also prepares for seamless content migration, ensuring only relevant, high-performing assets are transferred during the enterprise website relaunch.
Content Migration
Content migration is the process of transferring all relevant website content to a new platform as part of a website relaunch.
This process builds directly on the results of the content audit. Once outdated or irrelevant items are filtered out, teams can focus on moving only high-value and up-to-date content. This helps streamline the migration and reduces unnecessary clutter on the new site.
Depending on the site’s size and complexity, migration can be done manually, through automated tools (Cloudflare, UpdraftPlus, All-in-One WP Migration, etc.), or with custom scripts. Regardless of the method, preserving URL structures, applying proper redirects, and retaining SEO metadata are essential to avoid traffic loss.
Common issues include broken links, formatting problems, or content gaps, which is why thorough testing after the migration is key. Tools like Screaming Frog, CMS import/export features, or dedicated migration plugins are often used to support the process.
Information Architecture Planning
Information architecture (IA) Planning is the process of organizing, structuring, and labeling website content to make it easy for users to navigate and find information. During an enterprise website relaunch, this stage is essential for creating a user-friendly experience that aligns with business goals.
The process begins with understanding how users interact with the website. Through user research and persona development, teams identify key user needs and typical navigation paths, helping shape a logical content structure and clear user flows.
Next comes the inventory and categorization of existing content, often informed by earlier audit findings. By grouping content into relevant categories and subcategories, you create a foundation for building a clear sitemap and intuitive navigation.
The IA design includes developing a sitemap, defining menus and submenus, and choosing user-friendly labels. Wireframes are often used to visualize page layouts and test how users will move through the site.
User testing is a vital step in validating the structure. Feedback collected here helps refine the IA, ensuring that users can efficiently find what they’re looking for before the site goes live.
Accessibility Compliance
Accessibility compliance is the practice of designing and maintaining digital content that is accessible to everyone, including people with disabilities. For enterprise websites, it’s not just a legal requirement but also a commitment to inclusion, usability, and equal access.
Ensuring accessibility during a website relaunch means aligning your site with standards like the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
Enterprises should take a structured approach. Start with a combination of manual audits — ideally involving users with disabilities — and automated scans to catch common issues. Training your team on accessibility best practices ensures ongoing compliance, not just a one-time fix.
Gathering feedback directly from users with accessibility needs can uncover practical barriers and guide meaningful improvements. At the organizational level, it’s helpful to establish an internal accessibility policy, designate responsible teams, and publish an accessibility statement to show transparency and commitment.
Enterprise Website Redesign
Enterprise website redesign is a complete revamp of a large organization’s website, focusing on updating design, content, functionality, and technical systems. The goal is to enhance user experience, align with business objectives, and ensure the site’s scalability for future growth.
A website relaunch at the enterprise level typically signals that something substantial has or needs to be changed. The business may have evolved its positioning, entered new markets, launched new products, or shifted toward a more customer-centric model.
To be effective, the redesign must start with clarity.
What is the site expected to achieve in this new phase?
Are the goals to increase lead generation, improve conversion rates, boost user engagement, or unify fragmented content ecosystems across multiple business units?
Defining these objectives at the outset ensures that every decision — from structure to design to platform — contributes to a meaningful outcome.
Well-known enterprise website examples like IBM, Salesforce, or Adobe illustrate this point clearly. Their digital platforms are not only visually consistent and on-brand — they also serve a wide range of user journeys, from product exploration to onboarding, support, and thought leadership.
For companies embarking on a redesign, the process should be rooted in real data. This includes a close review of existing analytics, heatmaps, behavior flow, and feedback from end users and internal teams. Understanding how users currently navigate the site—and where they get stuck — helps identify high-impact opportunities for improvement.
At this stage, connecting the redesign with broader enterprise objectives is essential. For example, suppose the company is investing in digital transformation or entering a new industry vertical. In that case, the website must reflect those priorities through dedicated landing pages, new content architecture, and refined navigation.
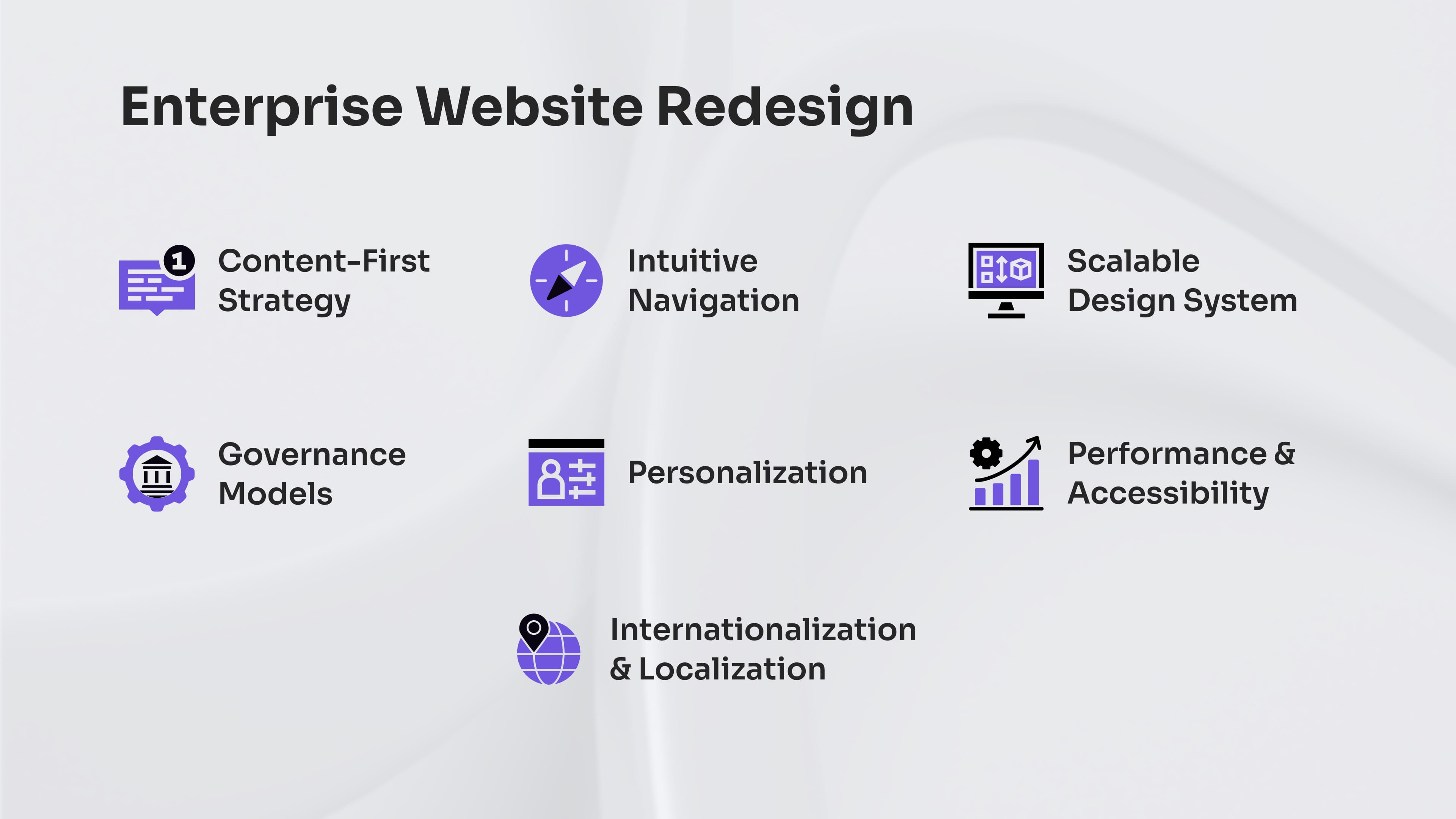
From there, several focus areas typically define a successful enterprise website design:
- A content-first strategy that prioritizes storytelling, brand messaging, and structured content to guide design and development decisions.
- Intuitive navigation and architecture that reflect the priorities of different user journeys and simplify complex site structures.
- A scalable component-based design system that ensures visual consistency, supports rapid iteration, and integrates seamlessly with modern CMS platforms.
- Robust governance models and approval workflows to support decentralized publishing and maintain brand integrity at scale.
- Personalization capabilities that allow for dynamic content delivery based on audience segments, behavior, or geography.
- Performance and accessibility standards that align with modern SEO, inclusivity guidelines, and enterprise-grade user experience expectations.
- Internationalization and localization support to ensure the site is relevant, compliant, and optimized for global audiences.
CMS Selection
CMS selection is the process of evaluating and choosing the most suitable content management system to support the structure, management, and delivery of content across an enterprise website.
An enterprise CMS is built to handle large volumes of content, support complex publishing workflows, and serve the diverse needs of multiple teams or departments. It provides a centralized environment where content can be structured, approved, and deployed efficiently, ensuring consistency, scalability, and long-term maintainability.
Selecting the right CMS means aligning the platform’s capabilities with business goals, user needs, and future growth. The right choice simplifies ongoing maintenance, supports collaborative content creation, and enables teams to deliver consistent experiences across channels and regions.
Choosing the right CMS depends on several factors:
- The size and complexity of your content operations;
- The level of customization and flexibility your team requires;
- Integration with CRMs, ERPs, and marketing tools;
- Governance needs and user permission structures;
- Scalability and support for global teams;
- Performance, security, and compliance requirements;
For organizations undergoing a relaunch, this is also a chance to reassess whether the current CMS still fits.
If it’s outdated, difficult to manage, or no longer aligned with future goals, migrating to a more robust enterprise CMS platform can make a significant difference in long-term success.
Technology Stack Setup
Technology stack setup is the process of selecting and configuring the foundational technologies (such as front-end frameworks, back-end infrastructure, databases, hosting environments, APIs, and third-party integrations) that will power your enterprise website after relaunch.
This step lays the technical foundation for future growth, performance, and maintainability. The right stack ensures your site is fast, scalable, secure, and flexible enough to support complex business logic, personalization, and third-party systems.
The setup is based on several factors:
- Business goals and technical requirements;
- Expected traffic volume and global reach;
- Integration needs with internal systems (CRM, ERP, etc.);
- Development team’s expertise and workflow preferences;
- Budget and long-term support considerations.
For modern enterprise websites, popular choices include:
- Front end: React, Next.js, or Vue.js for dynamic, fast-loading user interfaces
- Back end: Node.js, .NET, or PHP (often used with Symfony or Laravel)
- CMS: Enterprise-grade platforms like WordPress
- Hosting/Infrastructure: AWS, Azure, or Vercel for scalability and high performance
- DevOps tools: Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD pipelines for streamlined deployment
API Integration Plan
An API integration is the strategic roadmap for connecting your relaunched enterprise website to critical backend systems, such as CRM, ERP, payment gateways, and marketing platforms, through well-defined APIs.
A structured approach to enterprise integration ensures that all digital systems communicate effectively, enabling smooth data exchange, consistent user experiences, and uninterrupted business operations. Without a plan, API connections can cause issues like data inconsistencies, broken workflows, or security vulnerabilities, jeopardizing the success of the relaunch.
A robust plan defines the scope of each connection, selects appropriate API endpoints, establishes authentication and data formats, and schedules development and testing phases. It also lays out monitoring and versioning strategies to handle future API changes without disrupting site operations.
By formalizing scope definition, tool selection, implementation, testing, and ongoing maintenance, organizations can minimize risks, streamline complex workflows, and ensure that the relaunched website works harmoniously with existing enterprise systems.
Search Engine Optimization
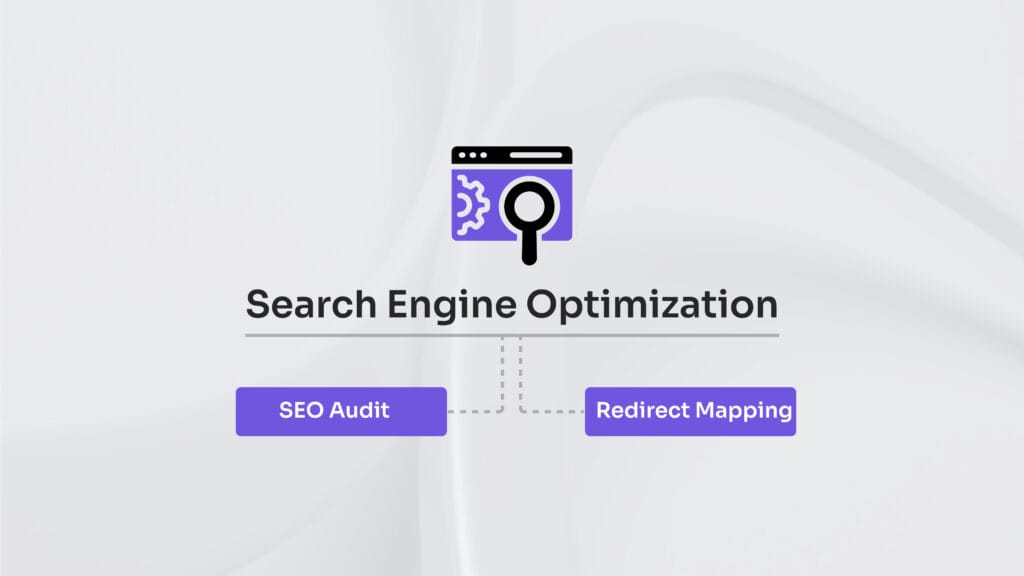
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of strategically refining a website and its content to improve visibility and rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs) for target keywords.
In the context of an enterprise website relaunch, SEO is closely tied to your broader content strategy and the insights uncovered during your content audit, ensuring that high-value pages are optimized and outdated or duplicate content is removed.
To launch successfully, begin with an SEO audit that assesses site structure, keyword performance, content quality (as defined by your content audit), and all technical SEO factors. This audit informs which pages need enhancement, consolidation, or removal, aligning your relaunch with search engine best practices.
Another essential component is redirect mapping. When URLs change during a homepage relaunch or full site relaunch, implementing 301 redirects according to your content migration plan preserves SEO equity, prevents broken links, and maintains both user experience and search rankings.
SEO Audit
An enterprise SEO audit is an in-depth evaluation of all the factors influencing the search performance of a large website, which includes reviewing site architecture, page speed, mobile-friendliness, keyword optimization, metadata, backlinks, and crawlability.
It also looks into deeper strategic areas like content quality, keyword alignment, and overall site authority. By analyzing these elements, the audit identifies strengths to preserve and weaknesses to address during the design relaunch.
The result of a thorough SEO audit is a detailed action plan.
This plan outlines the improvements needed to protect and enhance your SEO during and after the web relaunch. It highlights technical fixes, content optimizations, and structural changes necessary to ensure a smooth transition without losing search visibility.
When preparing to launch a new website, the audit acts as a critical foundation, helping enterprises avoid common SEO pitfalls and position the new website for immediate and long-term success.
Redirect Mapping
Redirect mapping is the process of carefully planning where each existing page should point once the new website is live. It ensures that no valuable traffic, SEO authority, or user journey is lost during the transition to the new website.
The decisions made during redirect mapping naturally reflect the broader content and design strategy. As the new site takes shape, the team reviews existing content, identifies what still serves the audience, and plans what needs to be updated or removed.
Redirects are carefully mapped to support this plan, guiding visitors to pages that offer the most current, relevant information and align with the new website’s communication style.
At the same time, the structure of redirects is influenced by the business goals behind the redesign. For example, if the focus is on improving lead generation, users might be redirected toward clearer, action-driven pages with strong calls to action.
If the aim is to build brand awareness, redirects might lead to richer storytelling sections that reflect the refreshed visual identity. In every case, redirects are not just technical fixes — they are part of shaping the user journey in a way that supports the larger ambitions of the relaunch.
Without proper redirect mapping, users could land on broken pages (404 errors), resulting in lost trust and diminished SEO rankings. When planned and executed correctly, redirects preserve the authority of existing URLs, maintain search engine rankings, and guide visitors smoothly to the most relevant content on the new website.
Enterprise Website Security Measures
Enterprise website security measures encompass the strategies, technologies, and protocols implemented to protect an organization’s digital assets during and after a website relaunch.
A website relaunch often involves significant changes, including new features, integrations, and design overhauls. These changes can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly managed. Implementing comprehensive security measures during the relaunch process helps prevent potential breaches, data loss, and service disruptions.
To protect against these threats, several key technologies and practices should be prioritized during a relaunch:
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: Establish strong perimeter defenses to monitor and block malicious activity.
- Strong Access Controls: Adopt a Zero Trust model, where no user or system is automatically trusted, and strict authentication is required.
- Regular Security Audits: Continuously evaluate the website and underlying infrastructure for vulnerabilities.
- Employee Training: Educate teams about phishing, password hygiene, and other security basics to strengthen internal defenses.
- Secure Hosting: Choose hosting providers that prioritize security with up-to-date infrastructure and proactive monitoring.
- Compliance with Frameworks: Align practices with standards like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework to meet regulatory and industry requirements.
Quality Assurance Testing
Quality Assurance (QA) Testing is the process of systematically reviewing and validating a website before launch to ensure it meets functional, technical, and user experience standards.
QA testing identifies issues like broken links, malfunctioning forms, performance bottlenecks, and accessibility gaps — all before users encounter them. Starting early in the development process, it helps create a more reliable, polished, and user-friendly website while minimizing costly post-launch fixes.
Beyond functionality, QA testing checks usability, accessibility, performance under different conditions, and overall site security — ensuring the website is resilient and inclusive.
Two key priorities for enterprise-level QA are thorough cross-browser testing to ensure consistent platform performance and full mobile responsiveness to deliver a seamless experience on any device.
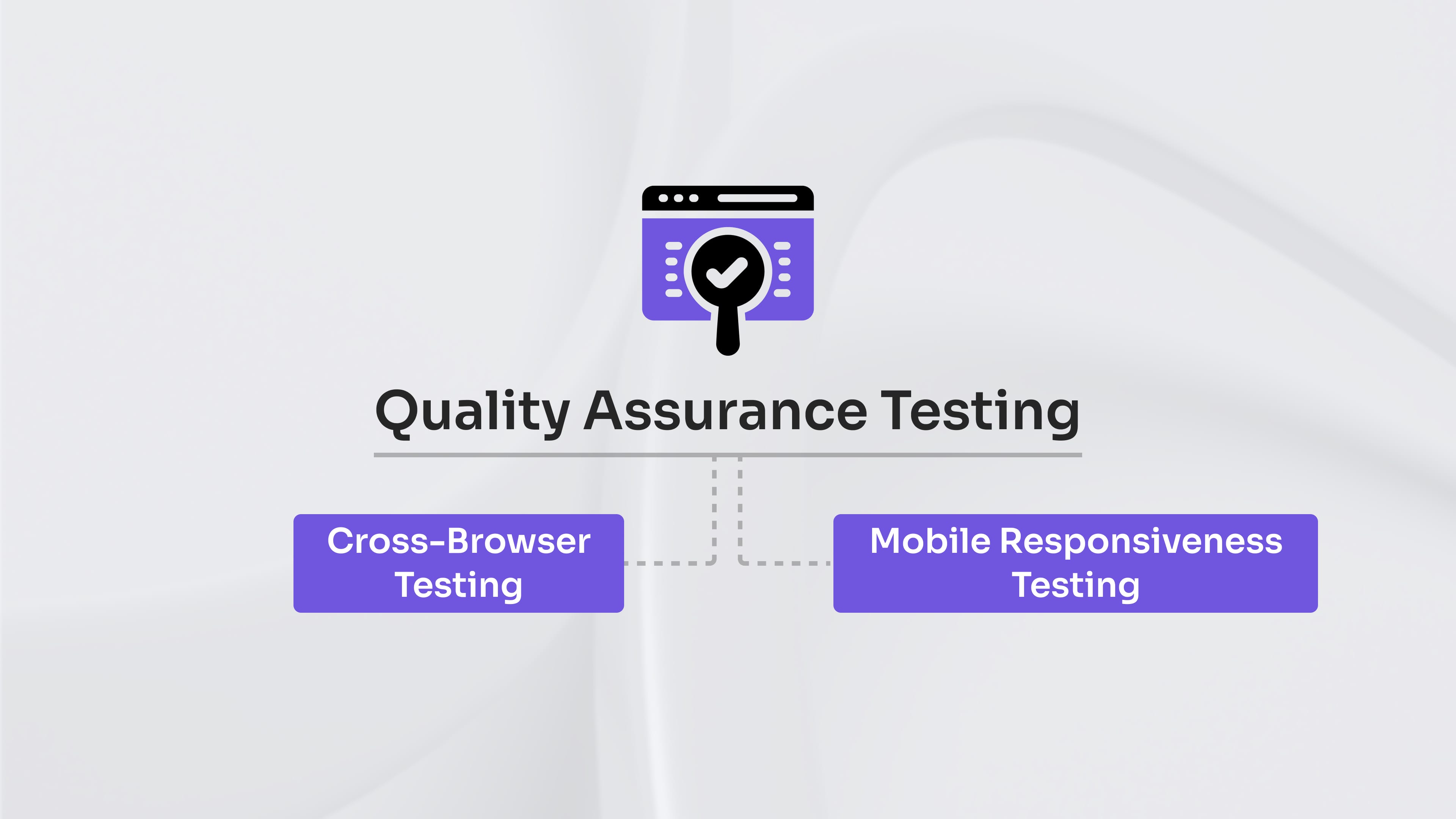
Cross-Browser Testing
Cross-browser testing is the process of checking whether a website works correctly and consistently across different browsers, devices, and operating systems.
Its main goal is to ensure that every user — no matter what browser they choose — has the same seamless experience when visiting the site.
This is crucial because browsers like Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Edge can interpret code slightly differently, which may cause inconsistencies in layout, functionality, or performance.
Without cross-browser testing, even a well-designed website can suffer from broken elements, distorted layouts, or inaccessible features for certain users.
By identifying and fixing these issues early, businesses improve overall website quality, enhance accessibility, reduce costly fixes after launch, and ultimately boost user satisfaction and conversion rates.
Cross-browser testing can be performed manually, by inspecting the site in different environments, or through automated tools like Selenium, which speed up the process and ensure more consistent results.
Mobile Responsiveness Testing
Mobile responsiveness testing is the process of evaluating how a website adapts and functions across different mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets.
This testing ensures that users get a smooth, visually consistent experience no matter what screen size, resolution, or mobile platform they are using.
Through mobile responsiveness testing, quality assurance teams check elements like layout adaptability, image scaling, text readability, button sizes, touch responsiveness, and load speeds on various devices.
They look for issues such as content overflow, broken navigation, or performance lags that can frustrate users and hurt engagement.
This process helps businesses deliver a consistent user experience, strengthen brand perception, and support better SEO performance — as search engines prioritize mobile-friendly websites.
Enterprise Website Launch Preparation
Enterprise website launch preparation is the process of systematically getting a site ready for public release by ensuring it is functional, secure, optimized, and aligned with business goals.
It is a critical stage that builds on thorough planning, testing, and strategic execution — and it heavily depends on the complexity of the website, the underlying business systems, and the organization’s scalability needs.
Effective preparation covers several key areas:
- Pre-Launch Testing: Every feature, link, and integration must be tested across different browsers and devices to catch errors early and ensure a smooth user experience.
- Content Review: All content should be proofread, checked for accuracy, and optimized for readability and engagement.
- Site Speed Optimization: Images, code, and third-party scripts are optimized to ensure fast load times, supporting both user satisfaction and SEO performance.
- Security Measures: SSL certificates are installed, vulnerabilities are addressed, and security protocols are tested to protect user data and maintain trust.
- SEO Strategy: Proper keyword research, metadata, sitemaps, and on-page optimizations are essential to help the website perform well in search engines from day one.
- User Experience (UX) and Mobile Responsiveness: Navigation must be intuitive, forms easy to use, and designs must adapt seamlessly across all screen sizes and devices.
- Analytics Setup: Tools like Google Analytics are configured to monitor site performance and user behavior post-launch.
- Backup Systems: Reliable backup protocols are established to safeguard content and data in case of technical failures.
A successful enterprise launch also includes enterprise-specific considerations:
- Scalability: The website must be built to support large volumes of traffic and future business growth without performance degradation.
- Integration: The site should seamlessly connect with business-critical systems like CRM, ERP, and marketing automation platforms.
- Customization: Role-based access and content personalization should be built in to meet different user group needs.
- Advanced Reporting: Implementing dashboards and complex data visualization tools enables better decision-making and performance tracking.
Enterprise Website Post-Launch Monitoring
Enterprise website post-launch monitoring is the continuous process of tracking, maintaining, and improving a website’s performance, security, and functionality after it goes live.
This phase is critical to ensure the website operates smoothly, supports business goals, and delivers a consistent user experience over time.
Post-launch monitoring includes several key activities:
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously tracking website speed, responsiveness, and uptime to catch and address performance issues before they impact users.
- Security Monitoring: Regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, applying security patches, and protecting the site against emerging cyber threats.
- Content and Functionality Checks: Ensuring that all links, forms, and interactive elements remain functional, and that content stays accurate and up-to-date.
- User Experience (UX) Monitoring: Analyzing user behavior, collecting feedback, and making iterative improvements based on real-world interactions.
- Performance Optimization: Identifying bottlenecks and opportunities for enhancing speed, scalability, and overall efficiency.
- Bug Fixing and Updates: Quickly addressing any bugs or technical issues that arise post-launch and keeping software components updated.
After the initial excitement of launch, ongoing monitoring ensures that the site continues to perform efficiently, providing users with a smooth and reliable experience. It helps detect and resolve technical issues, security vulnerabilities, and performance bottlenecks early, minimizing downtime and preventing potential disruptions to business operations.
Regular monitoring also supports continuous improvement by identifying areas for optimization based on user behavior and feedback. In addition, it helps maintain the website’s alignment with business goals by ensuring that all functionalities remain effective and up-to-date.
Without consistent post-launch monitoring, a website can quickly become outdated, vulnerable to threats, and less effective at serving users and driving results.
Enterprise Website Maintenance
Enterprise website maintenance is the ongoing process of updating, improving, and securing a website to ensure it remains functional, relevant, and aligned with business needs over time. It goes beyond simply monitoring performance — it involves actively managing technical updates, content improvements, security enhancements, and system integrations.
Regular maintenance keeps the website secure, user-friendly, and competitive. It ensures that security patches are applied promptly, content stays fresh and accurate, and new features or improvements are integrated as business requirements evolve.
Without proper maintenance, even a well-built website can experience technical failures, security breaches, and decreased user engagement, ultimately affecting business performance.
Enterprise website maintenance includes:
- Software Updates: Applying updates to the CMS, plugins, and third-party integrations to ensure compatibility and security.
- Security Management: Implementing security patches, monitoring threats, and reinforcing data protection measures.
- Content Updates: Refreshing or adding new content to maintain relevance and engage visitors.
- Performance Optimization: Continuously improving page speed, load times, and overall user experience.
- Backup Management: Regularly backing up the website to safeguard against data loss.
- SEO Updates: Adapting to search engine algorithm changes and optimizing new content for discoverability.
- Feature Enhancements: Introducing new functionalities and tools based on user needs and business growth.
While post-launch monitoring focuses on tracking the website’s performance, functionality, and security after it goes live, enterprise website maintenance is about actively maintaining and improving the website over its entire lifecycle. Monitoring is largely observational and reactive — identifying and responding to issues — whereas maintenance is proactive, ensuring the website evolves, stays secure, and continues to meet strategic goals.
What is the Difference Between Enterprise Website Relaunch and Relocation?
The key difference between an enterprise website relaunch and relocation is that a relaunch involves overhauling design, content, and features to enhance user experience, while relocation focuses on transferring the website to a new hosting environment or domain without changing its core functionality.
A website relaunch involves a complete overhaul or significant update of an existing website. This process typically focuses on enhancing user experience, improving functionality, updating content, optimizing for new technologies, and aligning the website with current business goals or branding strategies.
A relaunch can include redesigning the website’s layout, updating its code, improving site navigation, enhancing SEO, and incorporating new features or integrations. The goal of a relaunch is to improve performance, user engagement, and overall functionality, often following a period of stagnation or following substantial business growth or rebranding.
Website relocation, on the other hand, refers to moving the website from one hosting environment or domain to another. This could mean changing web hosts, transferring from an on-premise server to the cloud, or shifting to a new domain name.
Relocation primarily focuses on technical aspects such as ensuring minimal downtime, maintaining SEO rankings, and migrating data and content smoothly. Unlike a relaunch, which is a comprehensive redesign, relocation is more about logistics and the physical or virtual positioning of the website, often done for performance improvement, scalability, or cost-efficiency.
Contact
Don't like forms?
Shoot us an email at [email protected]

Send a Project Brief
You need to load content from reCAPTCHA to submit the form. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Turnstile. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Facebook. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from Instagram. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from X. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information

